HR leaders often encounter these pain points when selecting HR technology:
- Complexity: Challenges in finding suitable tools for diverse employee groups (shift workers, office staff, remote teams)
- Inefficiency: Data silos, redundant work, and errors in HR management due to lack of interconnected systems
- Scalability: Need for a flexible, scalable solution to support growth or market expansion
- Integration: Limited integration with ERP systems, production control, or other business applications
- Compliance: Growing importance of regulatory and data privacy requirements, especially in highly regulated industries
In this article, we’ll explore various components of HR tech, provide examples, and illustrate how each component can address daily HR challenges. This guide will help you determine the specific HR technologies your organization truly needs.
What is HR Tech?
HR-tech, short for HR technology, refers to technological advancements aimed at the HR sector, typically through software solutions or IT services. HR professionals rely on these solutions for effective workforce planning and management. Core elements include time tracking, workforce demand analysis, HR analytics, and recruitment tools.
The State of the HR Tech Sector
Digital HR solutions are instrumental in tackling societal challenges, like labor shortages. This is highlighted in Gero Hesse’s "HR Tech Overview DACH," which reported a 57% increase in HR tech companies within the DACH region, reaching a total of 489 firms in 2023.
The report also notes frequent acquisitions by larger industry players, especially when smaller HR tech providers face insolvency. However, investment in the sector remains relatively rare. GFOS stands out due to an investment from Riverside, a prominent growth equity investor, which reinforces the strength of their product and company. “The entry of such a renowned and successful growth equity investor is a confirmation of our first-class product and the entire company,” says Katharina Van Meenen-Röhrig, Co-CEO of GFOS Group. These investments underscore the growth potential in the HR tech market.
Moreover, Fortune Business Insights projects a 9.2% growth in the HR technology market through 2032, driven largely by the automation of HR processes. Artificial intelligence also plays a growing role: 58% of HR leaders are already collaborating with IT teams to identify use cases for AI in HR.
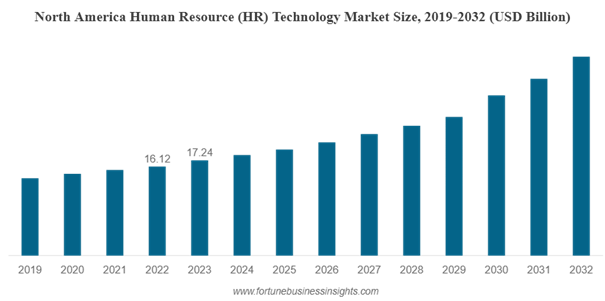
Growth of the HR Technology Market in North America; © Fortune Business Insights
Why Building an HR Tech Stack Makes Sense
Many tasks in HR can be automated or digitized, giving HR leaders valuable time to focus on more strategic responsibilities. This shift not only increases operational efficiency but also elevates HR management to a new level. The result: more time for what truly matters, enhancing retention efforts and driving employee satisfaction.
Here are some key advantages of a well-designed HR tech stack:
- Digitalization: Automating and digitizing manual, often administrative processes that consume daily work hours
- Analytical Capability: Leveraging workforce analytics and HR metrics to gain insights into trends and developments that support strategic decision-making
- Employee Satisfaction: Enhancing communication and streamlining internal HR workflows to promote collaboration, recognition, and retention
- Scalability: Adapting to organizational growth, regulatory changes, or evolving HR trends
- Competitiveness: Utilizing HR technology innovations and optimizing HR workflows to strengthen employer branding
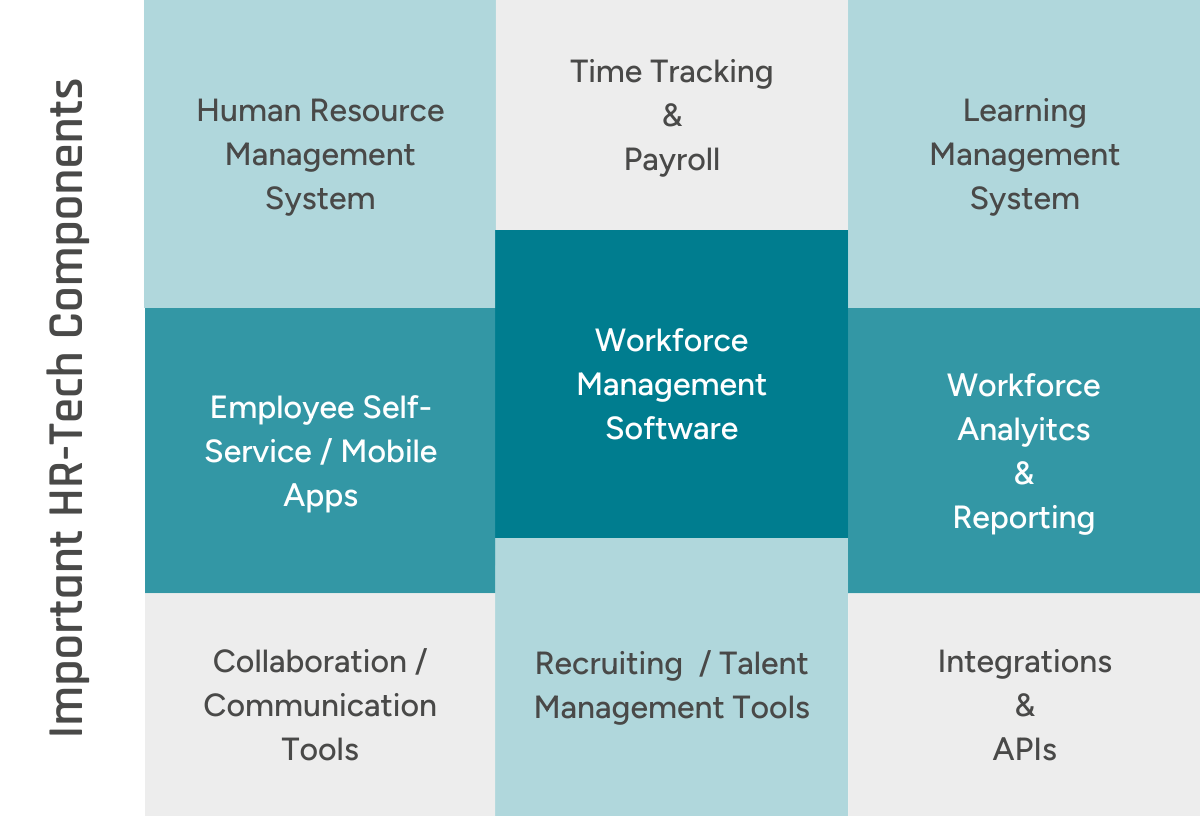
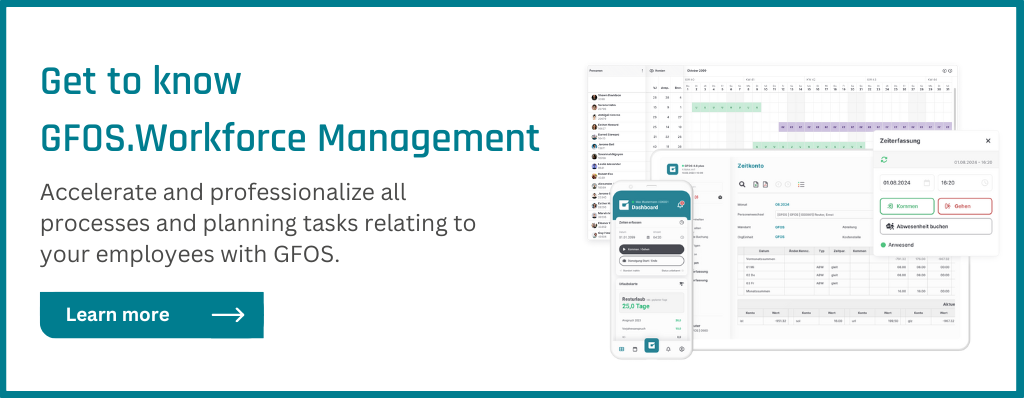
HR technology solutions should always be tailored to specific business needs; Image © GFOS Group
Building an HR Tech Stack: Key Components
A well-matched HR tech stack drives efficiency by automating and simplifying HR processes. Ideally, it’s scalable to support company growth while creating a work environment that fosters employee loyalty.
In short, choosing the right technology is essential for sustainable, successful HR management. The following components are crucial depending on industry and company size.
Human Resource Management System (HRMS)
A Human Resource Management System (HRMS) is a foundational element of any HR tech stack, providing centralized management of employee data and processes. It enables efficient handling of all HR-related data, supporting strategic decision-making and transparent reporting.
- Function: Centralized management of employee data, processes, and compliance requirements
- Key Uses: Payroll, time tracking, document management, absence- and attendance tracking
- Benefits: Increased efficiency, centralized data management, compliance with HR regulations
Payroll & Time Management
Payroll and time management systems are integral to HR technology. They help companies seamlessly manage payroll processes across systems, ensuring accuracy in wages, overtime, and bonuses, all while complying with labor laws.
- Function: Digitalization of payroll, time tracking, project time tracking, attendance planning
- Key Uses: Accurate payroll calculations, compliance with labor laws, management of bonuses, incentive pay, and overtime
- Benefits: Reduced errors through automation, time savings by minimizing manual processes, risk management (taxes, labor laws), and support for diverse working time models
Learning Management System (LMS)
A Learning Management System (LMS) provides companies with a platform to efficiently deliver and manage training and development programs. Using training management tools, companies can organize and distribute essential learning content, while skill management software tracks employee competencies, ensuring training aligns with each individual's needs.
- Function: Facilitates the delivery and management of training programs, central storage of skill records
- Key Uses: Internal and external training, certification programs, professional and personal development
- Benefits: Planning and distribution of learning content, customized learning paths and certifications, skill database, reminders for skill and certification refreshes
Workforce Management (WFM)
A Workforce Management (WFM) system is a key component for efficient staff scheduling, especially in less flexible environments like blue-collar sectors. An essential element of the HR tech stack, WFM enables centralized management of shifts, attendance tracking, and integration with other HR technology systems. Some providers, such as GFOS, also offer extensions for access control and manufacturing execution systems (MES).
- Function: Manages workforce scheduling, time and attendance tracking, project time tracking, integration with MES and access control systems
- Key Uses: Optimized shift planning, time management, resource planning, compliance with labor laws
- Benefits: Increased operational efficiency, flexibility in sectors like manufacturing, cost-productivity balance, support for complex time and shift models
Employee Self-Service (ESS) & Mobile Apps
An Employee Self-Service (ESS) portal allows employees to handle personal and administrative tasks independently. Through an ESS portal or mobile app, employees can access work records, pay stubs, and vacation balances, submit requests, and update personal details. This reduces HR’s burden from routine inquiries and ensures seamless communication across HR processes. Managers can also access these tools, often called HR self-service, to review key HR metrics and approve or deny requests.
- Function: Access to HR data, digital requests, efficient approval processes, reporting, remote work time tracking
- Key Uses: Increased transparency, reduced HR workload for routine tasks
- Benefits: Efficient HR workflows, enhanced employee satisfaction, remote work capability, productivity boost
Workforce Analytics & Reporting
Incorporating analytics and reporting systems into HR technology provides data-driven support for strategic decisions. This component centralizes and visualizes critical workforce data, identifying trends, patterns, and improvement areas. Key HR metrics, like turnover rates and absence rates, become more transparent, allowing proactive adjustments.
- Function: Analyzes HR data for strategic decision-making, visual representation in HR dashboards
- Key Uses: Monitoring KPIs such as turnover, absenteeism, and motivation metrics, integration with workforce planning
- Benefits: Data-driven decisions, trend analysis, risk factor identification, strengthening employee engagement through optimized HR processes
Collaboration and Communication Tools
Collaboration and communication tools are vital to the HR tech stack as they support teamwork and communication, especially in hybrid work models and dispersed teams. These tools enable employees to connect and collaborate from any location, fostering productive teamwork across sites in real-time.
- Function: Facilitates communication between employees and teams, collaboration across hybrid or decentralized teams, joint document work
- Key Uses: Team collaboration, internal communication, employee engagement
- Benefits: Supports modern work models, promotes teamwork across locations, enhances employee well-being, adaptable work culture
Recruiting & Talent Management System
A recruiting and talent management system streamlines the entire hiring process, from job posting to onboarding. Centralizing all applicant-related activities, it enables a structured recruitment workflow while ensuring data compliance. Automating recruitment tasks also speeds up hiring, enhancing the candidate experience.
- Function: Manages the entire recruitment process from job posting to hiring, ensures data compliance, identifies talent for open positions
- Key Uses: Optimized candidate sourcing, improved recruitment efficiency
- Benefits: Structured hiring process, faster time-to-hire, data-based insights for informed hiring decisions
Integration Interfaces for Other Systems
Integration interfaces are essential for connecting HR technology with other business systems, such as Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) for production control or ERP systems for enterprise resource planning. These integrations create a seamless data flow, ensuring alignment across work schedules, shift planning, production requirements, and other processes.
- Function: Integrates HR technology with other business processes, meets industry-specific needs
- Key Uses: Industry-specific requirements, efficient shift and resource planning, linking diverse data sets (e.g., production and payroll costs)
- Benefits: Aligns workforce needs with other business operations, reduces costs, increases productivity and competitiveness, enhances business insights
Time Tracking Explained: A Feature Found Across HR-Tech Components
Time tracking is a core function present in multiple categories of an HR tech stack, supporting various functions in different contexts. Its placement often depends on a company’s specific needs and the systems it uses. Because of this, different HR tech providers offer time tracking solutions. Selecting the right HR tech stack and providers is crucial for a tailored fit.
For example:
- Time tracking in HRMS focuses on administrative aspects of working hours, such as tracking hours worked and processing wages. Providers in this category are typically chosen by companies with “traditional office work” environments, where the primary need is to monitor payroll, overtime, and breaks.
- Time tracking in Workforce Management (WFM) adds functionalities for optimized scheduling, shift monitoring, and aligning with production targets. This time tracking integrates more deeply into the company’s day-to-day operations, particularly in industries with complex shift systems, specialized requirements, or additional tools like an HR self-service portal.
Conclusion:
Choosing between time tracking as part of an HRMS or WFM solution depends heavily on operational needs. If your focus is on optimized scheduling and integration with additional systems or functions, a workforce management provider may be a better fit—often referred to as “time management.” For companies with fixed hours and low demands on time model complexity, HRMS time tracking may be sufficient.
Choosing Your HR Tech Stack: Sample Guide
Selecting the right HR technology involves considering industry-specific needs, company size, and other critical factors. By doing so, you can effectively combine different systems, taking a decisive step toward enhancing organizational efficiency and future-readiness. Below is a brief overview.
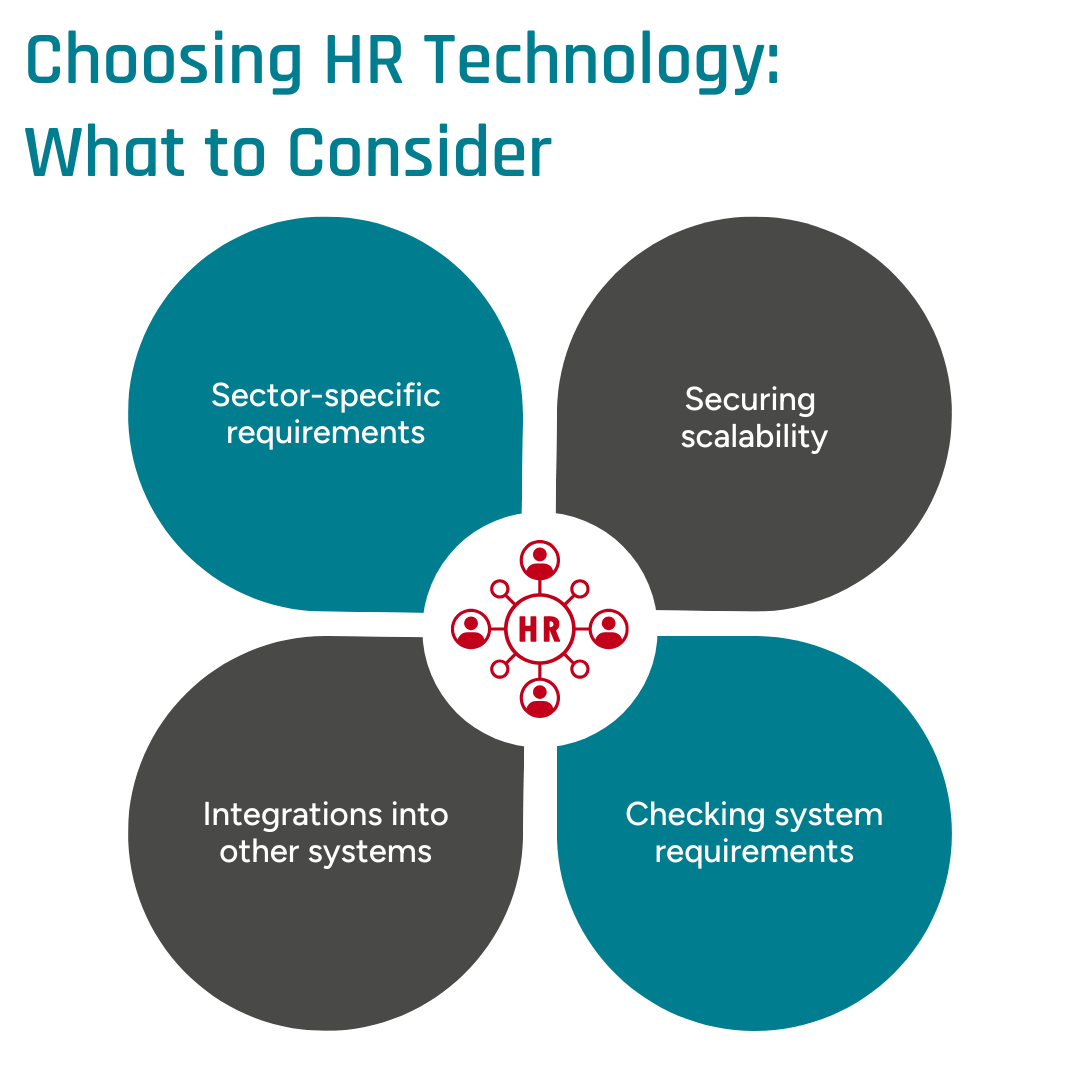
Various criteria are essential when implementing HR technology within a company; Image © GFOS Group
Consider Industry-Specific Requirements
Different sectors have unique requirements. Here are some examples by industry:
- Manufacturing: Integration with ERP and MES solutions for shift scheduling, labor costs (including piecework and incentive pay), and flexible scheduling that balances employee needs with production demands.
- Retail: Flexible shift and duty scheduling accessible via mobile, allowing employees to adjust shifts or swap with colleagues as needed, and handling seasonal demand fluctuations seamlessly.
- Service Sector: Performance management and project time tracking to ensure accurate billing; support for flexible hours and remote work capabilities.
- Healthcare: Flexible scheduling that considers patient load, special requirements for role-specific planning (e.g., ICU nurses), and 24/7 staffing for hospital patient care.
Ensure Scalability
Scalability is essential for growing businesses. The table below outlines examples that suit various company types, although these may not apply universally.
| Business size | Recommended solution | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| SMEs | Different cloud solutions | Scalable, low costs of implementation |
| Mid tier | Combination of cloud and on-prem solutions | Flexibility, cost efficiency, data sovereignty |
| Enterprise | Fully integrated systems with ERP-APIs | High adaptability, central monitoring |
Enable Integration with Other Systems
Comprehensive integration creates flexibility, transparency, and efficiency, helping companies become more agile and competitive. Therefore, it’s essential to assess existing systems and determine how new HR technology solutions can connect to them.
For instance, in the finance sector, skill management is a must. Financial service providers must ensure regulatory compliance through regular employee training for certifications and adherence to regulations. An integrated skill management system reduces the administrative load in this context.
Additional benefits of system integration include:
- Centralized Data Management: Connections between HR systems and operational platforms (such as ERP or CRM) ensure all departments work with up-to-date information
- Transparency and Responsiveness: Dynamic requirements, like workforce scheduling, can be quickly adapted to changing conditions
- Time and Cost Savings: Automation of administrative processes minimizes manual efforts and reduces potential errors
Define System Requirements
Companies must weigh factors like scalability and maintenance ease against data security and customization needs. This decision often comes down to choosing between a cloud-based or on-premise solution.
- Cloud Solution: Offers flexibility, scalability, and lower implementation costs, with external system maintenance—ideal for growing companies or those with multiple locations
- On-Premise Solution: Allows for higher data control and customization, though it requires more costly maintenance, IT infrastructure, and skilled staff—suitable for companies with stringent data security needs
The trend is shifting toward cloud migration, as more businesses embrace the flexibility of cloud solutions. Cloud systems are regularly updated, enhancing security and allowing for quicker implementation. This shift also facilitates the digitalization and automation of manual tasks, freeing up time for value-adding activities.
According to a KPMG study, HR departments spend approximately 70% of their time on administrative tasks that don’t contribute to business value.
Implementing HR-Tech in Your Company – 3 Steps for Success
Strategic planning and a structured approach are key to building an HR tech stack that delivers long-term benefits while minimizing risks.
- Plan a phased implementation: Start with a core system like time tracking, then gradually add modules such as shift scheduling or HR analytics. This allows for initial stability and early wins before expanding to additional components.
- Employee training: Even the best systems are only as effective as their users. A training program ensures that everyone—from HR staff to general employees—can use the tools effectively. This approach alleviates concerns and uncertainty through clear guidance.
- Continuous optimization: HR technology should be adaptable. Regular audits to assess new company goals or regulatory changes help ensure the system continues to meet both operational and strategic needs.
Integrate GFOS into Your HR-Tech Landscape
Leverage GFOS’s modular workforce management solution, connect to MES modules, and secure your organization with a reliable access control system. GFOS software as a scalable SaaS model has over 70 interfaces and a wide partner network for ideal compatibility.