What is Smart Maintenance?
The term smart maintenance covers all technologies and processes that enable a company to organize maintenance work more “intelligently”. The aim is to use comprehensive data from production to precisely determine when repairs or maintenance work should be carried out on machines.
The core of the concept is to continuously record and evaluate the actual condition of machines (using IoT sensors). This means that work is no longer only initiated after a machine has broken down; instead, such a breakdown is proactively prevented thanks to regular, intelligently planned maintenance intervals.
This proactive approach prevents costly machine and system downtime, which in turn is essential for the productivity, efficiency and profitability of a production facility. Companies that want to develop their production facilities into a smart factory in the medium term must therefore also consider the concept of smart maintenance.
Maintenance in Everyday Industrial Life - Typical Problems
As sensible and catchy as the principle of intelligent maintenance is in theory, it often encounters a number of practical problems in everyday business. Companies must first address these in a targeted manner in order to create a solid basis for the introduction of a smart maintenance concept.
Unplanned Stoppages and Downtime
If individual important machines fail, this can quickly lead to the entire production coming to a standstill. In many cases, this is the point at which the company reacts - usually in a hurry and with the aim of rectifying the production interruption as quickly as possible. In the rush, there is little scope for planned repair measures, if these do not already exist.Fragmented Information
The smart maintenance concept relies on relevant data - in digital form. However, many measures are still written down on paper or documented in individual Excel lists. In the worst case, only individual employees are even aware of the current status of a maintenance task. This lack of transparency quickly leads to work being carried out twice or not at all - both scenarios are uneconomical for companies to varying degrees.Lack of IT Expertise
Every IT solution stands and falls with the expertise of the employees implementing it. For SMEs in particular, the relative complexity of IT systems and the requirements for networking machines can pose a considerable challenge. Even today, people often shy away from this hurdle and stick with supposedly more convenient but inefficient solutions.- Maintenance by Calendar instead of by Need
In many companies today, maintenance work is anything but smart - machines and systems are maintained strictly by date, without taking into account the actual wear and tear of parts - or even being able to do so. This problem is also linked to the lack of reliable data, which means that either resources are tied up in premature maintenance tasks or measures are only taken once damage has already occurred.
In order for smart maintenance to be introduced and used effectively in companies, a rethink is needed in several areas - towards more data-based work, training employees in technological solutions and the willingness to systematically and permanently combine all of this into a holistic concept.
Smart Maintenance – What Characterizes the Concept
The concept of intelligent maintenance offers companies the opportunity to tackle the major problem of potential machine defects at a structural level. If intelligent maintenance is systematically introduced for the entire production process, this not only brings companies closer to the concept of the smart factory - it also gives them a significant advantage in direct competition.
Real-Time Condition Monitoring
In order to avoid unexpected machine downtimes and failures, the systems are monitored in real time. Sensors continuously collect operating data - such as temperature, vibration, pressure or energy consumption - and thus enable an immediate assessment of the machine's condition. This allows early intervention before machines break down or other damage occurs.- Predictive Maintenance
The “maintenance by date” approach that is still widely used ignores the actual condition of the systems - which, as described, often leads to unnecessary or late interventions. Predictive maintenance uses smart algorithms and historical machine data to predict faults at an early stage. This enables companies to carry out maintenance at the optimum time - not too early, not too late - and thus avoid unplanned downtime and expensive emergency measures. Intelligent Planning & Automation
An essential aspect of any smart maintenance concept is structural data collection. What used to be done on paper printouts or Excel lists is now collected and evaluated in detail with the help of the right software solutions. This broad database through the networking of numerous data sources enables largely automated decisions and maintenance planning - no more time wasted on manual coordination and the like.- Digital Knowledge Storage & Mobile Support in Everyday Life
The networking of production helps to sustainably break down existing data silos and make information centrally accessible to all relevant stakeholders. At the same time, it also supports the transfer of knowledge from skilled workers - long-standing knowledge about the maintenance and handling of machines is preserved so that this data will still be available to employees in the future. By storing the data in a cloud, this knowledge can be easily accessed both on site and on the move - for example during a customer appointment.
Enabling Intelligent Maintenance with MES Data
Implementing smart maintenance also requires innovative software solutions that continuously record maintenance-relevant data centrally. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) enable comprehensive data exchange between machine and software, as well as the analysis and visualization of the actual production status. This not only allows interval-dependent maintenance work to be scheduled at an early stage and taken into account in production planning: With the help of artificial intelligence, patterns and interdependencies in production can be identified from historical and real-time data and used for intelligent maintenance.
The analysis of machine, energy and process data provides information about deviations from normal values that could lead to disruptions in the short or long term. Production managers can initiate measures accordingly - long before regularly scheduled maintenance work - and thus prevent machine breakdowns. Particularly in the case of complex and networked systems, root cause analysis without corresponding software modules presents specialists with major challenges, as errors can often only be identified with enormous effort. However, with the help of dashboards, those responsible can always keep an eye on the most important events and relevant KPIs.
Some smart maintenance systems already initiate various maintenance measures independently and automatically take them into account in production planning. The maintenance work is reported to detailed planning so that orders can be rescheduled in good time, transports can be rescheduled and personnel resources can be deployed elsewhere. The database on which the artificial intelligence is based is constantly growing - evaluations and forecasts become increasingly precise over time and ensure faster response times and maximum efficiency.
The Advantages of Smart Maintenance - At a Glance
In practical application in companies, the following points in particular speak in favor of the concept of intelligent maintenance:
Better Availability / Less Downtime
The machines and systems involved in the process are continuously monitored, potential failures are detected at an early stage and rectified in good time. This increases availability and therefore overall equipment effectiveness.More Efficient Use of Resources / Lower Costs
Thanks to the establishment of a smart maintenance process, all maintenance is now carried out consistently according to need and not simply by date. As a result, materials and personnel are deployed in a highly targeted and cost-efficient manner.Greater Transparency / Better Traceability
Thanks to the right software solution, all maintenance processes and machine statuses are now digitally documented and can be called up at any time. In this way, everything remains traceable and verifiable.- Greater Resilience of Production
The unspecific risk of production downtime is effectively reduced to a minimum when a smart maintenance concept is consistently implemented. This mix of optimized availability through regular maintenance and low downtime risks makes your own production fit for the future.
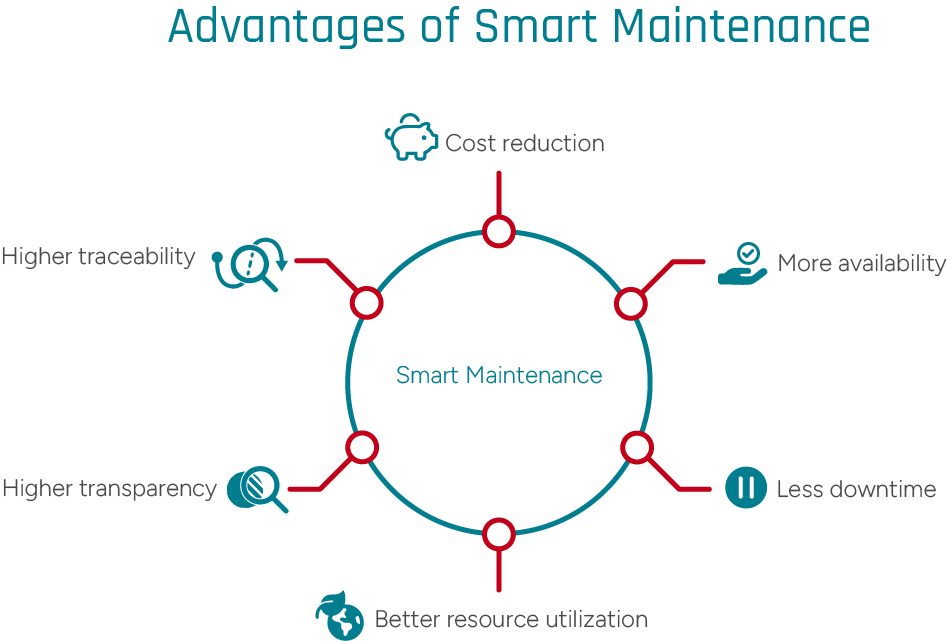
The smart maintenance approach offers companies a range of benefits - from lower costs to higher availability. © GFOS Group
Intelligent Maintenance - The Scenario Comparison
In the following scenario, we want to give an example of the difference such a smart approach to maintenance makes in practice.
Without Smart Maintenance - Production Interruption due to Undetected Wear
A manufacturer of precision components for mechanical engineering relies on manual visual inspections and maintenance according to a maintenance schedule. A worn ball screw is overlooked on a CNC milling machine. During series production, the component fails, leading to faulty milling processes and the shutdown of an entire production line.
Due to this failure, orders have to be rescheduled and finished parts have to be reworked - resulting in increased material usage, delivery delays and dissatisfied customers. Depending on the type of orders affected by this failure, inadequate machine maintenance can even result in long-term reputational damage for the company.
With Smart Maintenance - Continuous Production Without Interruption
The manufacturer of precision components has been relying on a combination of a modular MES solution and AI in production for some time now. As part of this conversion of its production, it has also established a data-supported smart maintenance system. This now monitors the operation of critical components such as ball screws in real time.
Sensors analyze vibrations, noise behavior and running times, among other things. When the first anomalies are detected, the system reports the need for maintenance. Replacement takes place proactively within the planned production window, without any unplanned interruptions. The quality of the parts produced, the company's own adherence to deadlines and, last but not least, operational reliability are guaranteed.
Are you interested in an intelligent maintenance solution?
Let us advise you individually!

