Method, Style, and Technique – Understanding the Differences?
In real-world practice, the lines between leadership styles, methods, and techniques are often blurred. However, a clear understanding of each term helps leaders use them more effectively.
- Leadership methods describe how leadership is structured and practiced across the organization. They define consistent principles and workflows for decision-making and communication.
- Leadership styles refer to the way individual leaders interact with their teams. The chosen style can strongly impact team morale, productivity, and the overall work environment—both positively and negatively.
- Leadership techniques are the tools leaders use in practice. These include performance reviews, goal-setting meetings, or advanced approaches such as 360-degree feedback.
In today's fast-changing work landscape, understanding and combining these elements is more important than ever. With growing skills shortages and increasingly hybrid teams, leaders must learn how to effectively communicate with a diverse workforce.
Strong leaders stand out by knowing how to align leadership methods with types of leadership styles to drive both employee satisfaction and business success.
What Influences Effective Leadership?
Leadership requirements vary by industry. Highly regulated sectors like healthcare or aviation rely on structured leadership and clear protocols to ensure safety and compliance. In contrast, creative industries often benefit from agile, flexible leadership styles that encourage innovation and experimentation.
Company Culture and Values
An organization’s values and cultural norms strongly influence its leadership approach. In companies with open, trust-based cultures, collaborative leadership methods are more common. Where strict hierarchies prevail, more directive or authoritarian types of leadership tend to dominate.
Industry and Organizational Structure
Leadership requirements vary by industry. Highly regulated sectors like healthcare or aviation rely on structured leadership and clear protocols to ensure safety and compliance. In contrast, creative industries often benefit from agile, flexible leadership styles that encourage innovation and experimentation.
Team Skillsets and Age Diversity
Leading a team with varying experience levels and age groups can be challenging. Senior employees may expect more influence, while younger generations like Gen Z value transparency, inclusion, and workplace participation. Leaders must adapt their leadership and leadership styles accordingly to manage expectations and foster engagement.
Emerging Challenges and Transformation
Modern work is more diverse and decentralized than ever. Remote work and digital transformation are reshaping how teams operate. At the same time, issues like burnout and mental health have become more prominent. Leaders must be mindful of these challenges and select appropriate leadership methodologies to support team wellbeing and organizational resilience.
Overview of Leadership Styles – Common Approaches to Managing Teams
In day-to-day business, leadership can look very different from one company to another. The way managers engage with their teams depends largely on how they view their own leadership role and the organizational context in which they operate.
Below is an overview of well-established leadership styles, each with its own strengths, weaknesses, and practical applications.
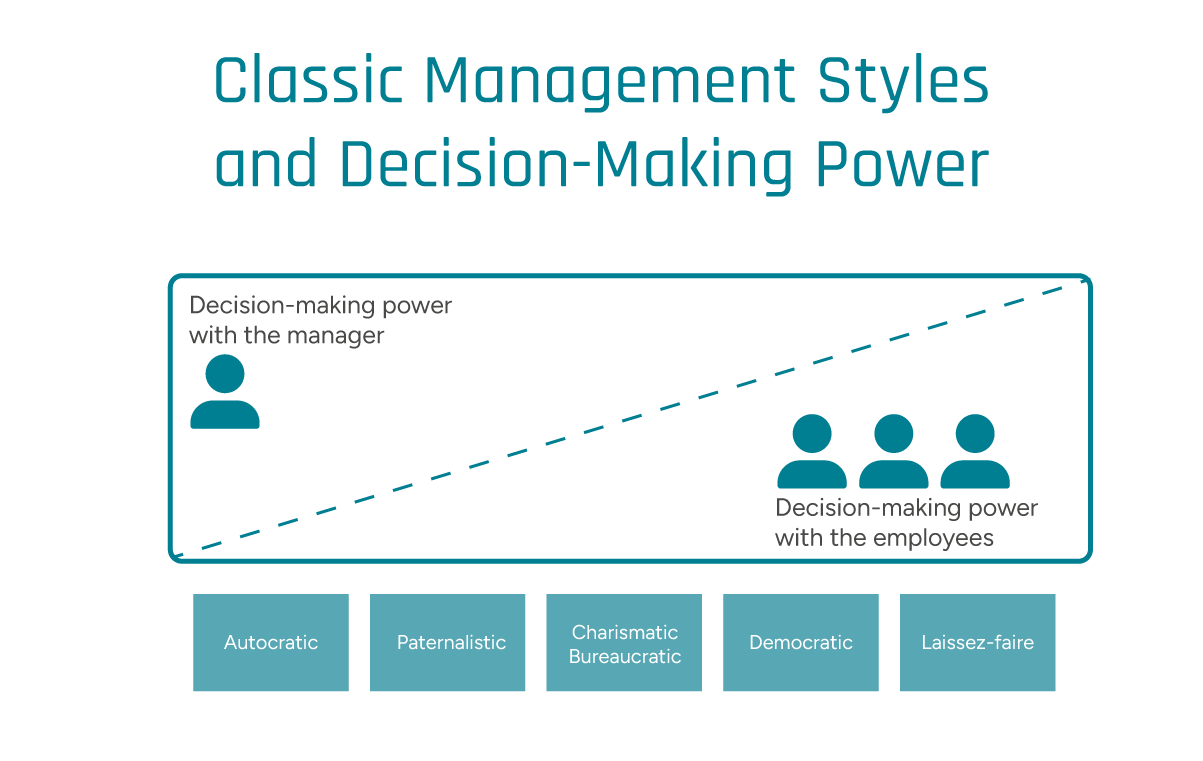
The different leadership styles can be categorized on a scale from more to less decision-making power on the part of the manager; Image © GFOS Group
Autocratic Leadership Style
The autocratic leadership style is characterized by centralized decision-making. Leaders operate with full authority, make decisions independently, and expect instructions to be carried out without question or feedback from employees. Team members typically have little to no input in decision-making processes.
This style is effective in high-pressure situations that require quick decisions and clear direction. However, it may suppress employee engagement, creativity, and initiative. In extreme cases, it can create a culture of fear if mistakes are met with punishment rather than support.
Democratic Leadership Style
This leadership method focuses on active employee participation. Team members are encouraged to contribute ideas, engage in discussions, and play a role in decision-making. Input is not just collected—it genuinely influences outcomes.
Democratic leadership styles promote motivation, trust, and innovation. However, this inclusive approach may slow down decision-making, particularly in urgent scenarios or when not all employees have the same level of knowledge or access to relevant information.
Laissez-Faire Leadership Style
Laissez-faire leadership involves a high degree of autonomy for team members. The leader provides general direction but avoids micromanaging or interfering in daily operations. They are available for guidance when needed but take a hands-off approach otherwise.
This type of leadership grants employees significant freedom, including in making key decisions. While it can work well for highly skilled or experienced teams, it may lead to confusion, lack of accountability, or inefficiencies—especially for less experienced staff who may require clearer structure and support.
Paternalistic Leadership Style
The paternalistic leadership style positions the leader as a caring authority figure, akin to a "father figure" within the team. Decisions are made with the intent of benefiting everyone, ideally creating a sense of security and direction for the group.
While this style can relieve pressure from the team and promote a supportive environment, it also centralizes a great deal of responsibility in the hands of one leader. If not carefully managed, this approach can become overly controlling, limiting individual initiative and creativity.
Charismatic Leadership Style
n this leadership style, the leader’s personal charisma is the driving force behind team motivation and cohesion. Through vision, passion, and strong communication, they inspire employees to rally behind shared goals and organizational values.
Charismatic types of leadership can energize teams and unlock high performance. However, they also carry risks. Overreliance on one individual may lead to instability if that person leaves or loses credibility. In some cases, charisma may even be used manipulatively, creating unhealthy dynamics within the organization.
Bureaucratic Leadership Style
A direct contrast to the charismatic approach, the bureaucratic leadership style emphasizes structure, rule-following, and consistency. Leaders rely on fixed procedures, detailed guidelines, and a strong adherence to organizational policies.
This leadership method fosters predictability and minimizes the likelihood of power misuse. However, the rigidity of this approach can limit innovation, slow down progress, and prevent employees from reaching their full potential if there is no room for creative input or flexibility.
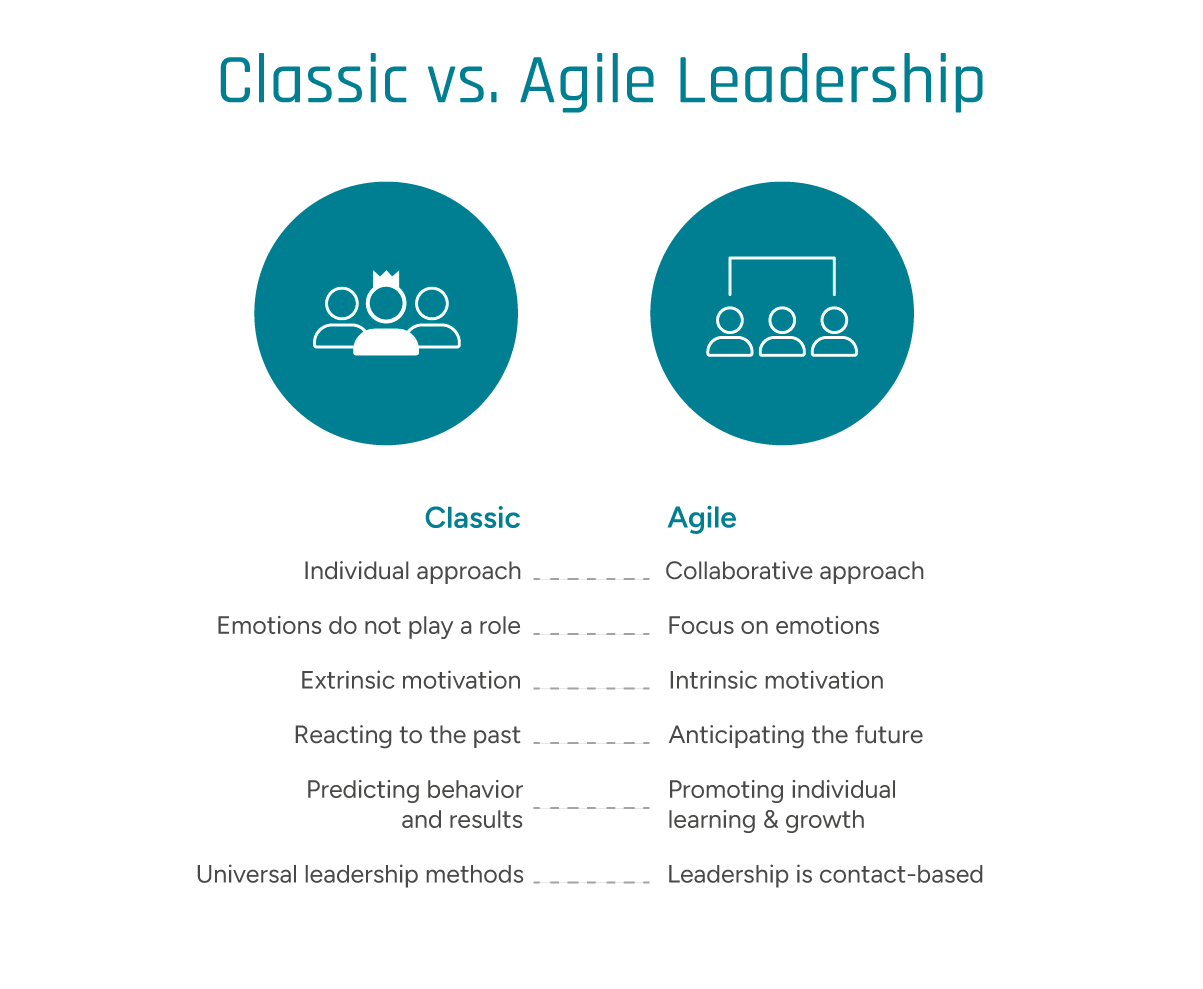
Modern leadership methods often differ significantly from traditional approaches to team management. Image © GFOS Group
Modern Leadership – Contemporary Approaches at a Glance
The types of leadership styles described above are based on classical theories from renowned psychologists like Kurt Lewin or sociologists such as Max Weber. These traditional models represent idealized forms of leadership rooted in hierarchy, control, and predictability.
In contrast, modern leadership styles emphasize motivation, shared values, and distributed responsibility—closely aligned with the New Work philosophy. Rather than focusing solely on direction and top-down objectives, the emphasis is on culture, mindset, and strategic alignment.
Deborah L. Ancona, Professor at the MIT Sloan School of Management, defines agile leadership as a leadership methodology built around four key capabilities:
- Sensemaking: Employees should understand the purpose and relevance of their work. This clarity creates engagement and can be reinforced through HR metrics and measurable outcomes.
- Relationship Building: Leaders must communicate openly and lead with empathy. They are expected to understand the perspectives of their team members and foster a positive, collaborative work environment.
- Visioning: Leaders create a strong team identity and unite employees behind a shared vision. This promotes a collective focus on long-term goals and future-oriented outcomes.
- Inventing: Leaders play a vital role in enhancing collaboration while also allowing room for innovation. They encourage breaking down outdated structures and exploring new ways of working.
In 2016, Jose Mathews, a lecturer at the Royal University of Bhutan, contributed to the discussion on modern leadership styles by highlighting the contrast between emerging and classical theories in his article New-Genre Leadership Theories. He described traditional leadership as rooted in authority, top-down control, and a resistance to change. Agile leadership, in contrast, is characterized by distributed responsibility, shared values, and an inherently motivational quality.
According to Mathews, cultivating a shared mentality within the company is crucial to inspiring individuals and helping them reach peak performance.
Emerging Leadership Methods – From Servant Leadership to OKRs
In addition to agile leadership, several other contemporary leadership methods have gained traction in today’s workplace. These include:
- Servant Leadership: The leader exists to serve the team, prioritizing employee needs and supporting personal development. In this leadership style, the manager works for their team rather than the other way around. The focus is on high job satisfaction and an empowering work environment.
- Situational Leadership: The style of leadership adapts to the specific context and the development level of each employee. This flexible leadership method allows for tailored support, but it also requires strong adaptability and emotional intelligence from the leader.
- OKRs (Objectives and Key Results): OKR is a performance-driven leadership and management approach where strategic goals are aligned with measurable key results. It fosters transparency, enhances accountability, and ensures all activities contribute to shared business objectives.
Where Do Different Leadership Styles Work Best? – Two Real-World Examples
The effectiveness of any leadership style depends heavily on the industry, work environment, and team dynamics. Different situations require different approaches. Below are two practical examples from everyday business operations:
- Agile Leadership in IT and Software Development: Project teams in the IT or software industry often rely on agile frameworks such as Scrum or Kanban. These models favor flat hierarchies and empower team members to work autonomously. In this context, agile leadership methods are especially effective, as they encourage creativity, distributed decision-making, and continuous improvement. Here, leaders take on a facilitative role rather than issuing top-down directives.
- Authoritarian Leadership in Manufacturing: In production environments with shift work and standardized procedures, a highly structured leadership approach is often more appropriate. Smooth operations require clearly defined workflows and accountability. More directive types of leadership are well-suited to this environment, helping ensure deadlines are met and quality standards are maintained consistently.
Modern Leadership in Practice – The Role of the Right HR Tech Stack
As teams grow more diverse, global, and complex, it becomes increasingly difficult for leaders to apply modern leadership methods consistently while addressing each employee’s unique needs. That is why today’s effective leadership is strongly supported by digital solutions.
A well-designed HR tech stack plays a critical role in enabling leaders to apply contemporary leadership styles effectively. The following tools are especially valuable in practice:
Workforce Scheduling
Modern HR software enables shift planning based on employee qualifications, availability, and personal preferences. This improves scheduling accuracy, minimizes conflicts, and enhances employee satisfaction.
At the same time, workforce management tools give leaders real-time visibility into important KPIs. Workforce analytics systems and automated reports make it easy to monitor personnel-related metrics and ensure data-driven decision-making.
Time Tracking and Workload Transparency
Digital time tracking systems help leaders identify capacity bottlenecks, peak workloads, and unused resources. Real-time insights allow for transparent assessments of how labor is distributed across the team.
This transparency supports not only operational efficiency but also discussions around workload balance and employee wellbeing—both of which are vital components of sustainable leadership and leadership styles.
Employee Self-Service Tools
Self-service tools allow employees to update personal information, submit requests, or access documents independently. These systems empower employees, increase process transparency, and promote a culture of accountability.
From a leadership perspective, this reduces administrative workload and enables managers to focus more on strategic and people-oriented tasks—an important advantage for applying modern leadership methodologies effectively.
Workforce Analytics
With the help of workforce analytics, leaders gain deep insights into key metrics such as turnover rates or absenteeism. These indicators are crucial throughout the employee lifecycle and support proactive leadership.
Recognizing patterns early—such as rising stress levels or declining performance—allows leaders to intervene before issues escalate. This data-driven approach fosters continuous team development and helps leaders tailor their leadership styles to individual and organizational needs.
Empower Your Leaders with Smart HR Software
With GFOS, you can simplify or even automate the day-to-day challenges faced by your HR leaders. Our workforce management experts will help you build a modern HR tech stack that supports data-driven, people-first leadership across your organization.