The Definition of a Smart Factory
The smart factory concept is based on the most complete possible networking of all processes within a production or manufacturing plant. Collaboration between people and machines is optimized by intelligent IT systems to such an extent that maximum efficiency can be achieved in all work steps.
Some features are central to a smart factory:
- Networking: All processes are networked with each other and are coordinated centrally or decentrally. IoT devices and sensors provide a large amount of important information about all work processes. This often comes together on an MES dashboard for a better overview.
- Autonomy: No human intervention is required for many work steps within the smart factory. As the relevant processes are clearly defined, machines can tackle the tasks to be completed without further input. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) now plays a major role here.
- Self-Optimization: In a smart production environment, machines and systems are in constant communication with each other. The data obtained in this way can be used to constantly uncover and reduce further inefficiencies in processes.
- Real-Time: Thanks to constant communication between devices, centralized information from production is generated and exchanged in real time. With the help of edge computing (LINK) and similar technologies, this information can also be analyzed with low latency in order to make real-time decisions.
In addition to these aspects, many companies are already relying on digital twins. These represent digital replications of physical production facilities and make it possible to plan or simulate a wide variety of production scenarios in detail before actual adjustments are made to the process.
Smart Factory: Challenges during Implementation
A largely fully automated production plant - from logistics to production - is naturally of interest to many companies. However, there are still a number of key challenges on the road to implementation that stand in the way of practical feasibility:
System Discontinuities / Heterogeneous IT Landscapes
In reality, many IT systems in companies are a mix of hardware and software solutions from various providers. If a company now plans to standardize this diversity in a central direction, this can involve a considerable amount of time and money.Data Islands / Data Silos / Lack of Transparency
Very few store floor systems are designed for a complete exchange of data. A lot of information and data records are often isolated in individual “data silos”. This data must also be identified and evaluated in order to optimize processes holistically.Lack of Interoperability (Machines / Software)
Even today, different machines and systems still use data formats that are not necessarily compatible with each other. This can be the case with older systems and IT solutions in particular. The lack of open interfaces can make it difficult to exchange information and hinder networking.Change Management / Reservations of the Workforce
Such a far-reaching changeover as the transition to the smart factory must be communicated well and openly internally. Otherwise, it can be assumed that employees will be very skeptical about this change. Effective change management helps to emphasize the benefits and dispel concerns.
These problems require a differentiated approach in order to identify suitable and practicable solutions. After all, the digital transformation of individual companies cannot work without overcoming these challenges.
Solution Approaches for Smart Factory Concepts
The following approaches have proven successful in solving the above-mentioned problems:
IoT Integration / Networking of Machines
The availability of IoT devices and sensors significantly helps to drive forward the complete networking of plants and systems. All of this decentrally collected data is then brought together at a central location. The gradual switch to established industry standards (in terms of interfaces) further simplifies networking.Data Basis for Decisions / Real-Time Analyses
A central dashboard is needed within production - a hub where all information and data points from production flow together. The use of powerful software and hardware ensures real-time data analysis, which also reveals potential weak points in the process and incomplete information (e.g. due to data silos).- Modularization / Scalable Software Architecture
If systems are not fully interoperable, this problem can be solved with modular software solutions. The modularity of these software architectures ensures that they can be easily integrated and adapted to the respective intended use.
However, a sensible implementation of all these solution approaches is hardly conceivable without modern manufacturing execution software (MES). In many production companies, MES systems have long served as the central interface and control instance with which the entire production - and all relevant data flows - can be precisely tracked and controlled. A well-configured MES therefore forms the backbone of every smart factory.
Important Elements of a Smart Factory
A key aspect of the Smart Factory is the fact that such a system not only works autonomously, but is also self-optimizing. This cyclical structure of processes is reflected in the “Smart Factory Elements” model.
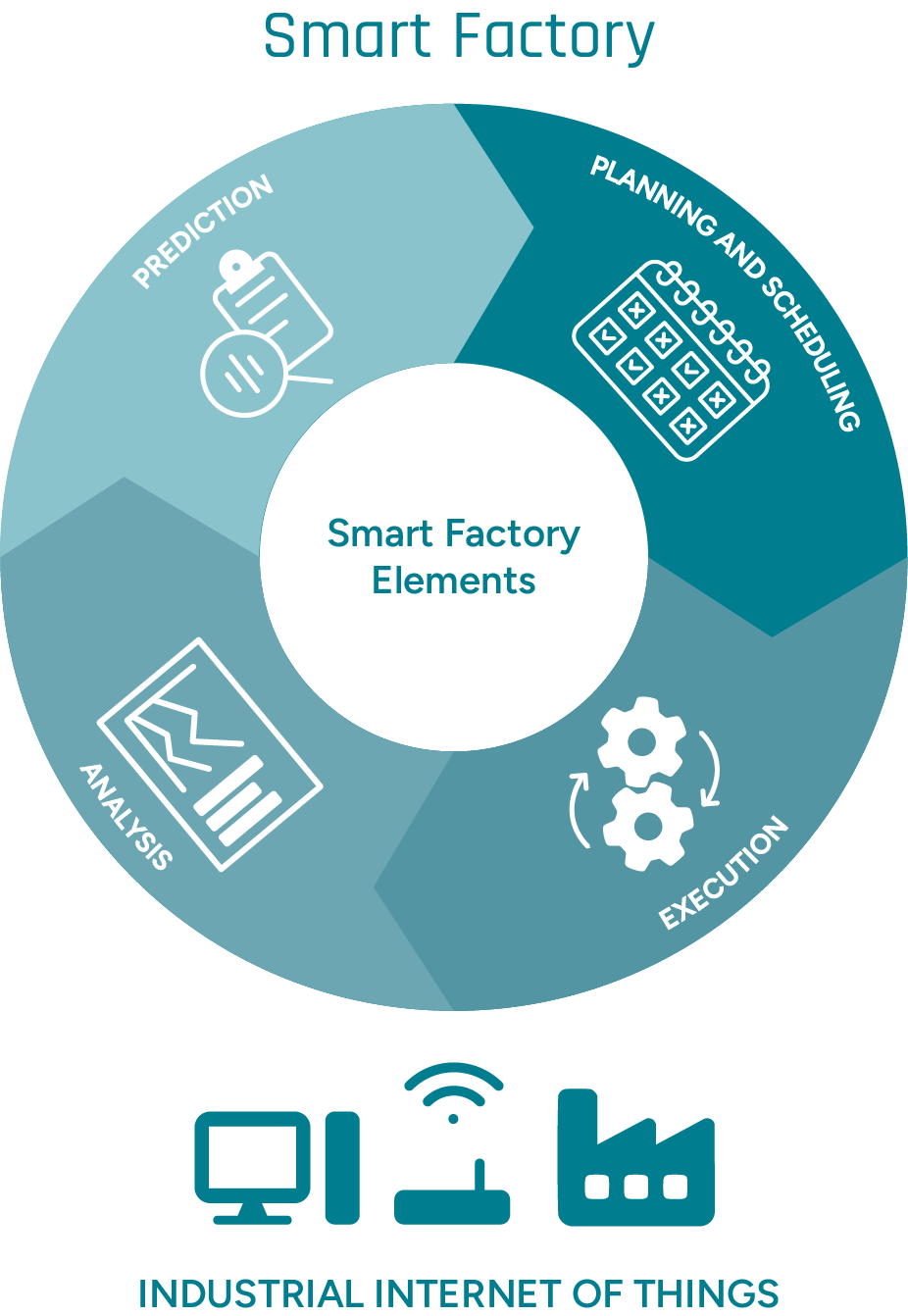
In the Smart Factory Elements model, all sections are part of a continuous optimization process of the Smart Factory as a whole. © GFOS Group
Prediction
This module includes the ability to predict future events or conditions based on historical and current data. Artificial intelligence, machine learning and predictive analytics can be used to forecast maintenance requirements, quality deviations or demand trends, for example. This allows companies to act proactively and not have to wait for problems to occur.
Planning
Planning and scheduling ensure that resources, materials and capacities are used efficiently. Intelligent algorithms and the integration of real-time data from the warehouse, production and logistics enable production plans to be dynamically adjusted and bottlenecks to be avoided. As a result, production remains both resilient and sufficiently flexible at all times.
Realization
After planning, this module focuses on operational implementation. Machines and employees work together, with their activities being coordinated by digital systems such as an MES. As part of operational implementation, process-related data is continuously collected and evaluated (IoT sensors) in order to identify and counteract any complications in real time.
Analysis
The analysis forms the conclusion - and at the same time the starting point - of the smart factory cycle. Here, production data is systematically evaluated, key figures are calculated and causes of deviations are identified. These findings are then used to refine forecasting models, adjust KPIs and identify optimization potential.
The Road to the Smart Factory - Key Questions for Companies
Before a company decides to make the transition to a truly intelligent production environment, there are a number of questions that those responsible for the project should ask themselves and answer honestly.
Taking Stock - Where do We Stand?
Entrepreneurs need to have a clear picture of the current status of their own production, recording and documenting machines and processes in detail. What technologies are already in place and how are they being used? Is networking and machine communication already in place? Are software solutions already being used in production?
There must also be a comprehensive exchange with the specialists and department heads at production level. This is where the crucial knowledge about the company's internal processes and workflows lies - and this is the only way to create a complete picture of the current situation.
Objectives - Where do We Want to Go?
To introduce Industry 4.0, a company needs two basic things. Firstly, digital production control in the form of a holistic manufacturing execution system to consistently record and collect all data. Secondly, there must be a clear vision for the corporate and product strategy. This is because the digitalization of the manufacturing industry not only leads to new, mostly automated logistics and production processes: it also opens up access to other markets and requires a concrete, digital business model.
A target state must be defined, on the basis of which a specification sheet for a smart factory can be created. This is the only way that MES consulting agencies or software providers can program and implement their knowledge, experience and ultimately their IT solutions in line with requirements.
Technology - How good are our Systems?
As Industry 4.0 is a digitalization project, it is clear that an IT infrastructure is fundamental to its introduction. Networks must be available with sufficient performance and signal strength so that data can be transferred in real time.
The basic IT landscape naturally also includes industrial PCs and databases. While on-premise solutions have mostly been used in the past, cloud and hosting services are becoming increasingly important. These offerings allow the setup and administration of IT infrastructures to be outsourced - saving money and resources.
Specialist Knowledge - Do We Have the Know-How?
The Smart Factory is a project that networks processes across departments and divisions. This therefore also means that there are (no longer) any isolated solutions and that the flow of information and knowledge must function both seamlessly and holistically.
Digital competence must be built up or expanded within the company - from the managing director to the employee, from the division manager to the specialist. This is not just about learning the new software and how it works, but also about topics such as data protection, information security and many other aspects.
Implementation - Where do We Start?
The digital transformation towards the smart factory is an industrial revolution and therefore a far-reaching intervention in business models and processes in industry. A step-by-step and area-by-area introduction is therefore advisable. If a manufacturing execution system is already in use, its range of functions and modules should be expanded as much as possible.
If only isolated solutions are currently in use, a professional MES solution should be introduced first - and attention should be paid to its Industry 4.0 and AI capability. Software providers usually offer IT solutions that can be adapted to industry and company size requirements. This means that the manufacturing execution system is flexible and can be adapted to new circumstances and requirements at any time.
From Theory to Practice - How Companies are Proceeding
Based on the above questions, many production companies are now working with step-by-step approaches to realize the concept of a smart factory in the long term.
Maturity Model
Especially at the start of the process, it has proven useful to objectively assess the current digital status of production with the help of a maturity model. Such models analyse dimensions such as IT integration, data availability, degree of automation or organizational maturity. The results of this analysis provide indications of strengths, weaknesses and development potential.Target Definition
Based on the maturity level analysis, the next step is to derive specific targets and fields of action - such as improved system availability, greater transparency or a higher degree of automation. This is the aforementioned “target state” that those responsible for planning should keep in mind.Selecting a Pilot Area
Every smart factory started small - instead of a comprehensive changeover, we recommend starting with a specific use case with high potential and manageable risk. This is where the previous considerations and ideas can be applied for the first time under real conditions.Evaluation & Scaling
All findings from the pilot project - positive and negative - are incorporated into further planning. If the concept is rolled out in other areas of production, best practices are continued and “old” mistakes are avoided. At the same time, of course, data will continue to be collected in this step.- Continuous Optimization
As the Smart Factory Elements model already illustrates, there is no end state on the road to the Smart Factory. Companies are faced with the constant challenge of continuously optimizing and gradually developing the system through data analyses, feedback loops and process improvements.
Important: Where companies are planning to make their production processes fit for the challenges of Industry 4.0, they need to keep three key factors in mind: They need the right technology, the right processes and capable, motivated employees.
Ultimately, all of these factors build on each other - and companies must be careful to consider all three factors in their planning projects. This is the only way to achieve a successful transformation to a smart factory.
